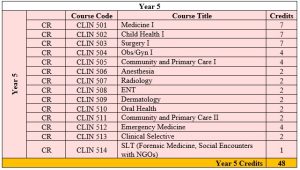
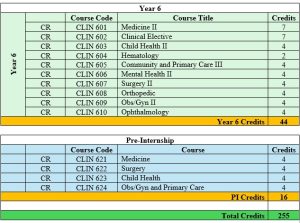
Plan of Study
The MD program presents a comprehensive medical education program (as depicted in the above POS) organized in a progressive, systems-based approach with several notable characteristics:
Curriculum Framework
The program follows a vertically integrated curriculum that begins with foundational basic medical sciences and gradually incorporates clinical experiences, culminating in a senior clerkship. The structure includes:
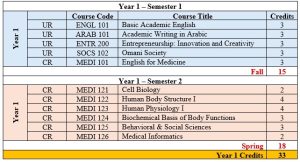
- Pre-medical foundation (Year 1) with both university requirements and medical prerequisites
- Basic medical sciences (Year 1) focused on normal human structure and function
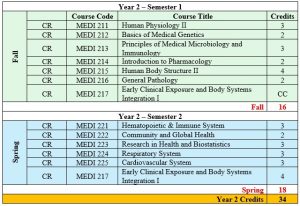
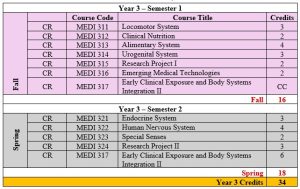
- Systems-based learning (Years 2-3) organized around major body systems
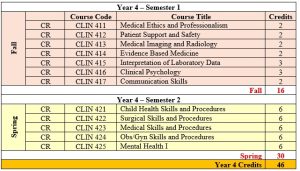
- Clinical phase (Years 4-6 plus pre-internship) with the final year dedicated to senior clerkship rotations and pre-internship
Distinctive Features
- Language and Cultural Integration: The curriculum uniquely balances regional context with global standards by including courses in Academic Writing in Arabic, Omani Society, and English for Medicine, emphasizing an institution serving the Sultanate.
- Early Clinical Exposure: Clinical integration begins in Year 2 through the “Early Clinical Exposure and Body Systems Integration” courses that continue into Year 3, indicating a spiral curriculum approach.
- Research Emphasis: The program incorporates research requisite (Biostatistics in Year 2) followed by progressive research projects in Year 3, developing scholarly capabilities alongside clinical skills.
- Modern Medical Education Elements: The curriculum includes contemporary aspects like Medical Informatics, Emerging Medical Technologies, and Community/Global Health, reflecting awareness of evolving healthcare needs.
- Entrepreneurship Focus: The program includes Entrepreneurship-Innovation and Creativity in Year 1, suggesting preparation for healthcare leadership and innovation.
Credit Distribution
The credit system appears carefully structured with:
- Higher credit allocations (3–4 credits) for fundamental science courses
- Clinical rotations in the later years having appropriate credit weight
- Longitudinal courses like Early Clinical Exposure using continuous credit (CC) designation
The curriculum design reflects modern medical education principles that emphasize early clinical relevance, systems-based teaching, research competencies, and professional development alongside traditional biomedical knowledge.